Understanding the four stages of the creative process
In the realm of human endeavor, creativity stands out as a dynamic force that fuels innovation, drives progress, and enriches our lives. At its core, creativity is a process—a journey of transforming novel ideas into reality. Understanding this process is essential for anyone looking to harness their creative potential or foster it within a team or organization.
In this story
Overview of the Creative Process
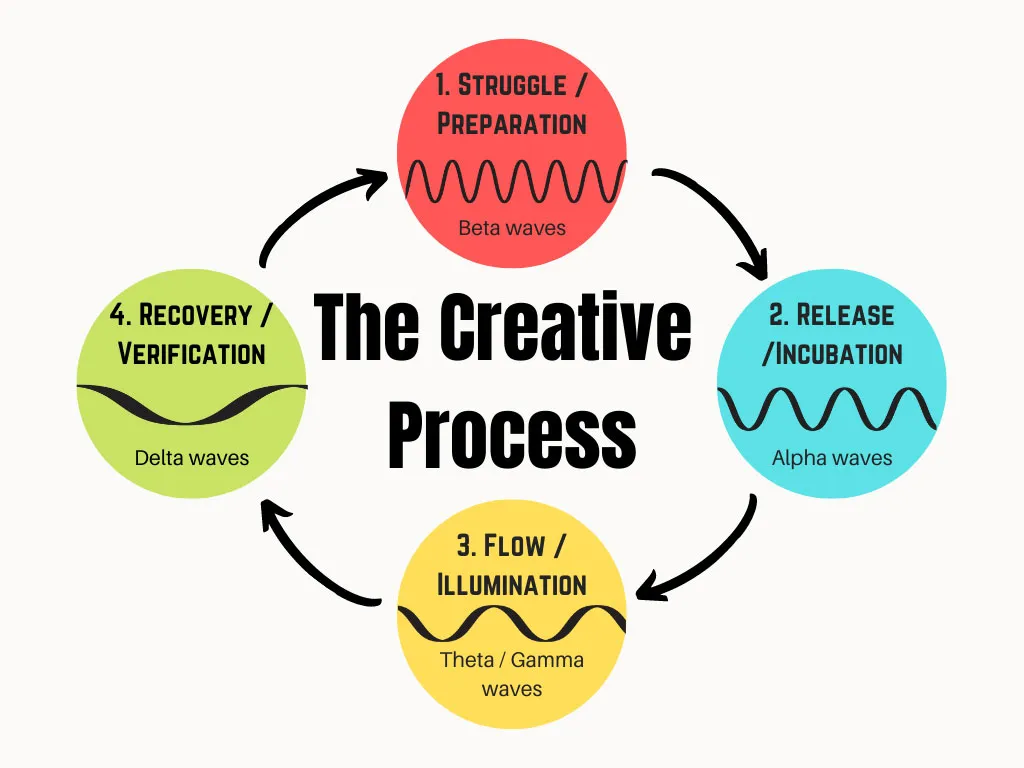
The creative process is often depicted as a series of stages that guide an individual from the conception of an idea to its realization. Traditionally, this process is broken down into four distinct stages: preparation, incubation, illumination, and verification. Each stage represents a unique phase in the journey of creativity, combining cognitive, emotional, and practical elements that contribute to the development of innovative ideas and solutions.
The preparation stage involves gathering information, identifying problems, and setting the groundwork for creative thinking. It requires an open mind and a willingness to explore diverse perspectives. Following preparation, the incubation stage allows the subconscious mind to process information, often leading to unexpected connections and insights. This phase highlights the importance of allowing time and space for reflection, as breakthroughs often occur when one is least consciously engaged with the problem.
Illumination, or the “aha moment,” is the stage where a creative insight suddenly emerges, often after a period of incubation. This sudden clarity is a hallmark of the creative process, bringing with it a sense of excitement and possibility. Finally, the verification stage involves evaluating and refining the idea, ensuring that it is both viable and valuable. This phase requires critical thinking and practical application to transform the initial spark of creativity into a tangible outcome.
Importance of Understanding Creativity
Understanding the creative process is crucial for several reasons. First, it demystifies the nature of creativity, dispelling the myth that it is solely the domain of artists or geniuses. By recognizing that creativity is a structured process, individuals can approach it with greater confidence and intentionality. This understanding empowers people to cultivate their creative skills, regardless of their field or background.
Moreover, understanding creativity enhances problem-solving abilities. In a world where challenges are increasingly complex and multifaceted, the ability to think creatively is invaluable. By leveraging the creative process, individuals and organizations can develop innovative solutions that address contemporary issues in unique and effective ways.
Additionally, fostering creativity within organizations can lead to a more engaged and productive workforce. When employees understand and are encouraged to engage with the creative process, they are more likely to feel valued and motivated. This can result in a culture of innovation, where new ideas are welcomed and nurtured.
In conclusion, the creative process is a vital component of human innovation and development. By understanding its stages and significance, individuals and organizations can unlock new potential, drive progress, and contribute to a more dynamic and creative world.
Stage 1: Preparation
The creative process begins with the crucial stage of preparation, where the groundwork is laid for the development of innovative ideas. This stage is characterized by active engagement with information and a keen awareness of the problems and opportunities that exist within a given context. By dedicating time and effort to preparation, individuals can set the stage for effective creative thinking.
Gathering Information
Gathering information is the cornerstone of the preparation stage. It involves a deliberate and systematic approach to collecting data, insights, and knowledge relevant to the area of interest. This process requires an open and inquisitive mindset, as information can come from a variety of sources, including books, academic journals, online resources, and conversations with experts or stakeholders. The goal is to build a comprehensive understanding of the subject matter, which serves as a foundation for generating creative solutions.
Effective information gathering goes beyond passive consumption; it involves critical analysis and synthesis of the collected data. By identifying patterns, trends, and gaps in the existing knowledge, individuals can gain deeper insights into the topic at hand. This analytical approach not only enhances understanding but also sparks curiosity and prompts further exploration. Additionally, engaging with a diverse range of perspectives and disciplines can enrich the information-gathering process, leading to more nuanced and innovative ideas.
Identifying Problems and Opportunities
Once a solid base of information has been established, the next step in the preparation stage is to identify the problems and opportunities that warrant creative exploration. This involves shifting focus from data collection to critical evaluation of the current situation. By examining the information through a problem-solving lens, individuals can pinpoint areas where improvements or innovations are needed.
Identifying problems requires a keen understanding of the challenges faced by individuals, organizations, or communities. It involves asking probing questions and considering the underlying causes of these challenges. This process often reveals opportunities for creative intervention, where innovative solutions can have a significant impact. Recognizing opportunities is equally important, as it involves envisioning potential enhancements or new directions that can be pursued.
This stage of the creative process benefits from a collaborative approach, where diverse perspectives can contribute to a more comprehensive understanding of the problems and opportunities. Engaging with others through brainstorming sessions and discussions can uncover insights that might otherwise be overlooked. Furthermore, maintaining an open mind and a willingness to challenge assumptions can lead to the identification of unconventional opportunities that hold great potential for innovation.
In conclusion, the preparation stage of the creative process is a critical foundation for generating innovative ideas. By gathering information and identifying problems and opportunities, individuals can position themselves to effectively engage with the subsequent stages of creativity. This stage requires curiosity, critical thinking, and a collaborative spirit, all of which contribute to a successful creative journey.
Stage 2: Incubation
The incubation stage of the creative process is a unique and often misunderstood phase where the seeds of innovation are nurtured in the subconscious mind. This stage follows the intensive information-gathering and problem-identification work of the preparation phase, allowing the creative mind to process the gathered material in a less direct, but profoundly effective way. Incubation is characterized by subconscious processing and the essential role of time and reflection in fostering creativity.
Subconscious Processing
During the incubation stage, the conscious mind takes a step back, allowing the subconscious to take over. This process involves the brain working in the background to form connections, synthesize information, and explore potential solutions without the constraints of active thought. Subconscious processing is powerful because it permits the mind to look at problems from different angles, free from the biases and limitations of conscious reasoning. This phase often occurs during activities unrelated to the problem at hand, such as walking, exercising, or even sleeping.
The strength of subconscious processing lies in its ability to integrate disparate pieces of information and generate novel associations that might not be evident through deliberate thinking. It is during this phase that the mind often arrives at unexpected insights and creative breakthroughs. This process underscores the importance of allowing the mind to wander and engage with different stimuli, as these can trigger the subconscious to produce innovative ideas.
The Role of Time and Reflection
Time and reflection play a critical role in the incubation stage. Unlike the more active phases of the creative process, incubation requires patience and trust in the subconscious mind’s ability to work through complex problems. This stage cannot be rushed; instead, it benefits from a period of detachment from the immediate task. Allowing time provides the subconscious with the necessary space to digest information thoroughly and form meaningful connections.
Reflection is also integral to this stage, as it involves periodically revisiting the problem with a fresh perspective. This reflective practice can occur naturally, often when one is in a relaxed state, which can lead to the “aha” moments of clarity. Engaging in reflective activities such as meditation, journaling, or quiet contemplation can facilitate this process, enabling the mind to consolidate thoughts and prepare for the illumination stage.
Understanding the incubation stage requires acknowledging that creativity is not solely a product of deliberate effort but also of allowing the mind to wander freely. By embracing the power of subconscious processing and the importance of time and reflection, individuals can enhance their creative capabilities and prepare for the insights that emerge during the next phase of the creative process. This stage highlights the importance of balance between active engagement and passive reflection in fostering innovation and creativity.
Stage 3: Illumination
The illumination stage of the creative process is perhaps the most exhilarating, marked by the arrival of the “aha” moment—an instance of clarity and insight that brings with it a sense of breakthrough. This stage follows the incubation period, where subconscious processing has laid the groundwork for a sudden surge of understanding and creativity. Illumination is characterized by the eureka moment and the subsequent recognition of creative insights.
The Eureka Moment
The eureka moment, often described as a flash of brilliance, is when a solution or idea suddenly crystallizes in the mind. This moment typically arrives unexpectedly, often when one is engaged in unrelated activities or in a relaxed state of mind. It is the culmination of subconscious processing during the incubation phase, where the mind has been quietly working to integrate information and form connections. When these elements coalesce, they result in a moment of profound clarity.
The eureka moment is not just about the sudden appearance of an idea; it is accompanied by a sense of excitement and confidence in the solution. This emotional response is crucial, as it provides the motivation and energy needed to explore the idea further. The spontaneity of this moment highlights the importance of allowing the mind the freedom to roam and the value of stepping away from problems to gain fresh perspectives.
Recognizing Creative Insights
While the eureka moment is thrilling, recognizing and validating the insights that emerge is equally important. Creative insights can sometimes be fleeting and may require immediate attention to capture their essence. It is essential to document these insights as they occur, whether through writing, sketching, or recording thoughts, to ensure they are not lost to the distractions of daily life.
Recognizing creative insights also involves assessing their relevance and potential impact. This process requires a balance between intuition and critical thinking, as not every idea will be viable or applicable. Evaluating insights involves considering their feasibility, alignment with objectives, and potential to solve the identified problem or leverage an opportunity. This discernment ensures that the creative process remains grounded while still embracing innovation.
The illumination stage is a testament to the power of the human mind to generate novel solutions and ideas. By understanding the dynamics of the eureka moment and recognizing the value of creative insights, individuals can effectively harness this stage of the creative process. This understanding enables them to leverage their moments of illumination to drive innovation and achieve meaningful outcomes in their creative endeavors.
Stage 4: Verification
The culmination of the creative process is the verification stage, where ideas born from the illumination phase are meticulously evaluated and refined to ensure their practicality and impact. This stage involves critical scrutiny and the transformation of abstract concepts into viable solutions that can be implemented effectively. Verification is essential to bridge the gap between creativity and real-world application, ensuring that ideas are not only innovative but also actionable and sustainable.
Evaluating Ideas
The first step in the verification stage is the thorough evaluation of ideas. This involves a critical assessment of the feasibility, relevance, and potential impact of the insights obtained during the illumination stage. Evaluating ideas requires a combination of objective analysis and subjective judgment, as the goal is to discern which concepts hold the most promise for development.
This evaluation process often includes criteria such as alignment with strategic goals, resource availability, cost implications, and potential market or user acceptance. Engaging diverse perspectives through collaborative discussions can provide valuable input, as it allows for the identification of strengths and weaknesses that may not be immediately apparent. Feedback from peers, stakeholders, or potential users can illuminate practical considerations that need to be addressed, ensuring that the idea is robust and viable.
Refining and Implementing Solutions
Once ideas have been evaluated, the next step is to refine and implement the chosen solutions. Refinement involves iterating on the initial concept to enhance its effectiveness and address any identified shortcomings. This iterative process often includes prototyping, testing, and gathering further feedback to fine-tune the solution. The goal is to create a well-developed version that is ready for implementation.
Implementing solutions requires careful planning and execution. It involves developing a strategy to bring the refined idea to life, which may include creating detailed action plans, allocating resources, and setting timelines. This stage is also where potential challenges are anticipated, and contingency plans are devised to ensure smooth execution. Effective communication and collaboration with all involved parties are crucial to align efforts and ensure that the implementation is successful.
Throughout the verification stage, maintaining a balance between creativity and practicality is essential. While the initial idea should remain true to its innovative roots, it must also adapt to real-world constraints and opportunities. This stage underscores the importance of flexibility and perseverance in the creative process, as continuous refinement and adaptation are often necessary to achieve the desired outcome.
In conclusion, the verification stage of the creative process transforms inspiration into reality. By carefully evaluating, refining, and implementing ideas, individuals and organizations can ensure that their creative efforts lead to meaningful and impactful solutions. This stage is a testament to the power of creativity when grounded in diligent and thoughtful execution.
Conclusion
As we conclude the exploration of the creative process, it is essential to reflect on the dynamic journey that creativity encompasses. This process, comprised of distinct yet interconnected stages, provides a structured approach to fostering innovation and generating impactful solutions across various fields.
Recap of the Creative Stages
The creative process begins with the preparation stage, where individuals immerse themselves in gathering information and identifying problems and opportunities. This stage lays the groundwork for creativity by equipping the mind with the necessary knowledge and context. Following this, the incubation stage allows for subconscious processing, where the mind works in the background to form connections and generate insights. This phase emphasizes the importance of time and reflection, providing the space for ideas to mature.
The illumination stage is where the “aha” moments occur—sudden flashes of insight that bring clarity and inspiration. These moments are the culmination of the subconscious work done during incubation and are characterized by a sense of excitement and breakthrough. Finally, the verification stage involves evaluating, refining, and implementing these insights to ensure they are viable and impactful. This stage bridges the gap between creativity and real-world application, transforming ideas into tangible outcomes.
Applying the Creative Process in Various Fields
The versatility of the creative process makes it applicable across a wide range of fields, each benefiting from its structured yet flexible approach. In business, the creative process drives innovation in product development, marketing strategies, and organizational design. By applying the stages of creativity, businesses can develop solutions that meet customer needs, anticipate market trends, and foster a culture of continuous improvement.
In the arts, the creative process is instrumental in producing original works that resonate with audiences. Artists across disciplines—whether visual, performing, or literary—utilize the stages of creativity to explore themes, experiment with mediums, and refine their expressions. The process allows for a depth of exploration and experimentation that leads to unique and compelling creations.
In education, the creative process is employed to develop engaging curricula and teaching methods that inspire students. Educators use creativity to design learning experiences that encourage critical thinking and problem-solving, equipping students with the skills necessary for the modern world. The process fosters an environment where students can explore, innovate, and learn from both successes and failures.
Similarly, in scientific research and technology, creativity is vital for advancing knowledge and developing groundbreaking innovations. Researchers and technologists apply the creative process to hypothesize, experiment, and iterate, driving progress in fields such as medicine, engineering, and environmental science.
In conclusion, the creative process is an invaluable framework that transcends disciplines, offering a pathway to innovation and problem-solving. By understanding and applying the stages of creativity, individuals and organizations can unlock their creative potential, leading to transformative outcomes that enrich our world. This structured approach not only nurtures individual creativity but also fosters collaborative efforts that drive collective progress and innovation.




Leave a Reply